How to make mock noises?
Noise-added mock cubes for Monte Carlo fitting
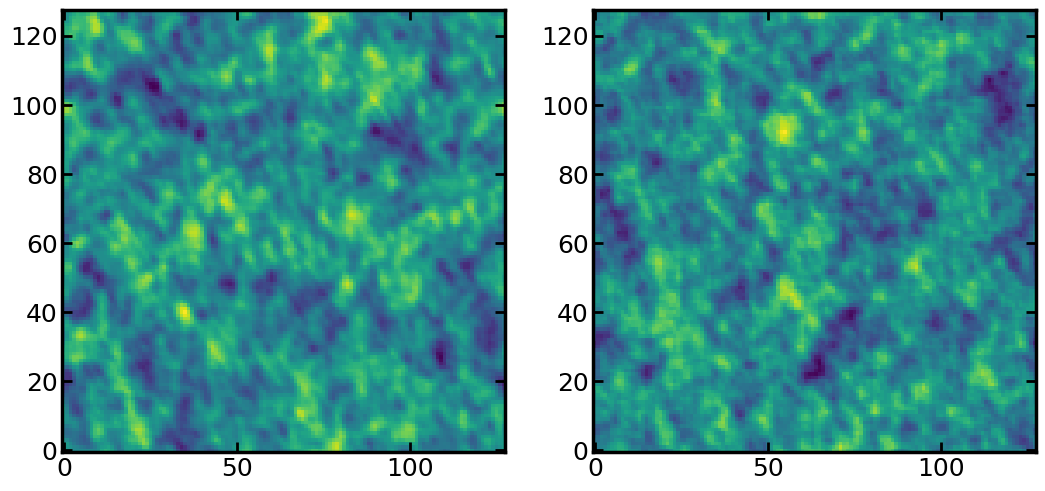
Tokult can add spatially correlated noise maps to the observed data. These noise maps have the same rms with the observed data. Tokult internally uses these noise-added data cubes for the Monte Carlo fitting method on the image plane.
from tokult import Tokult
tok = Tokult.launch('tokult_mockcube_dirty.fits', 'tokult_cube_dirty.psf.fits')
tok.use_region((32, 96), (32, 96), (5, 12))
cube_noise_added = tok.datacube.perturbed(tok.dirtybeam.fullconvolve)
The lensing parameters are not needed only to produce mock noises. Let’s compare the created noise-added cubes with the original data.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure(figsize=[6.28 * 2, 6.28])
ax0, ax1 = fig.subplots(1, 2)
ax0.imshow(tok.datacube.imageplane[0, :, :], origin='lower')
ax1.imshow(cube_noise_added[0, :, :], origin='lower')
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f77deea62b0>
Note that the shape of tok.datacube.imageplane is (7, 64, 64), so
tok.datacube.imageplane[0, :, :] contains the first channel map of
the object.